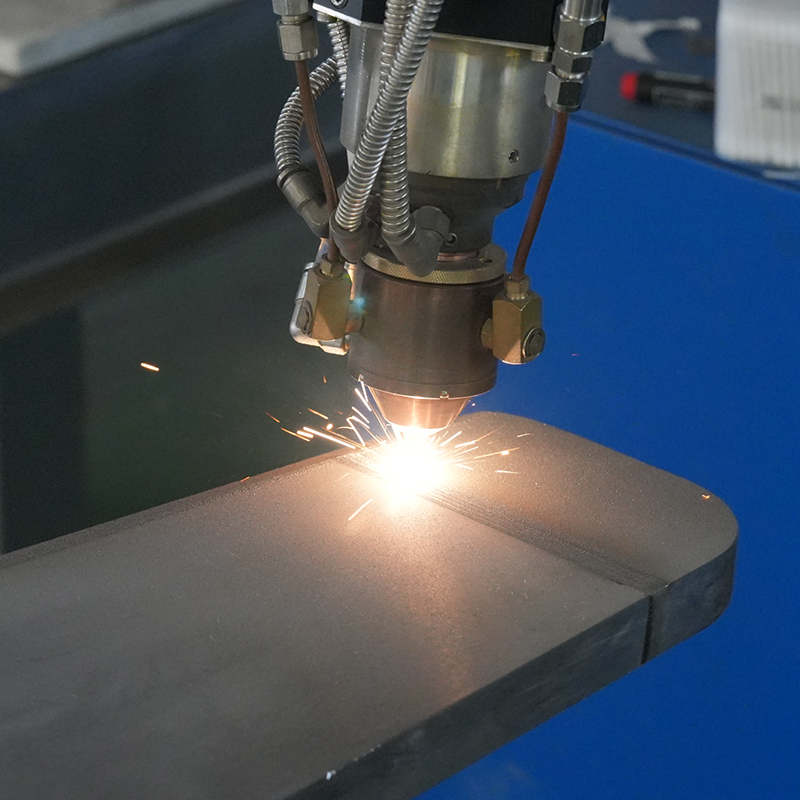
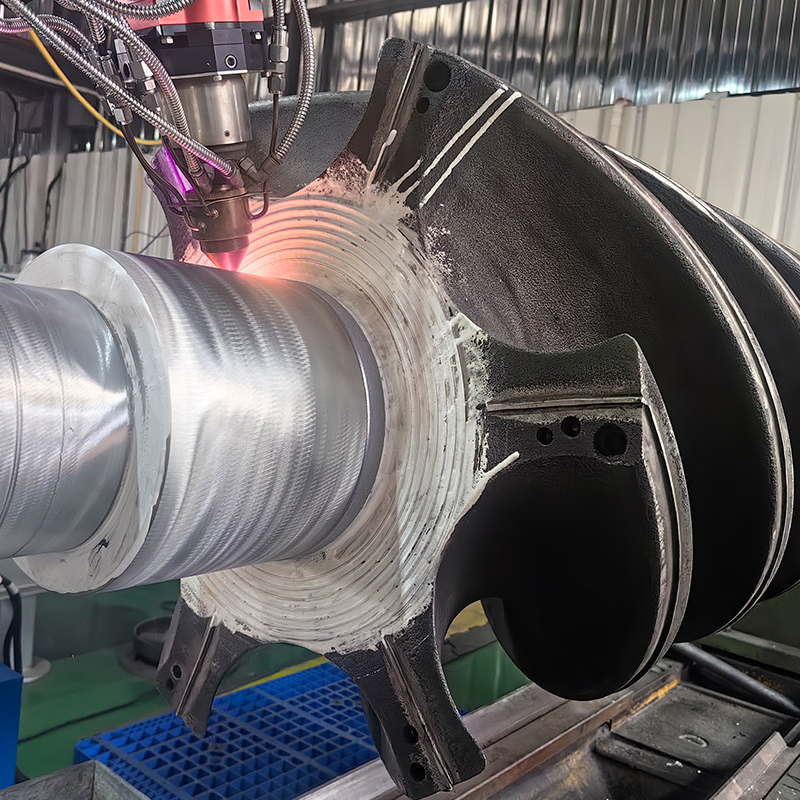
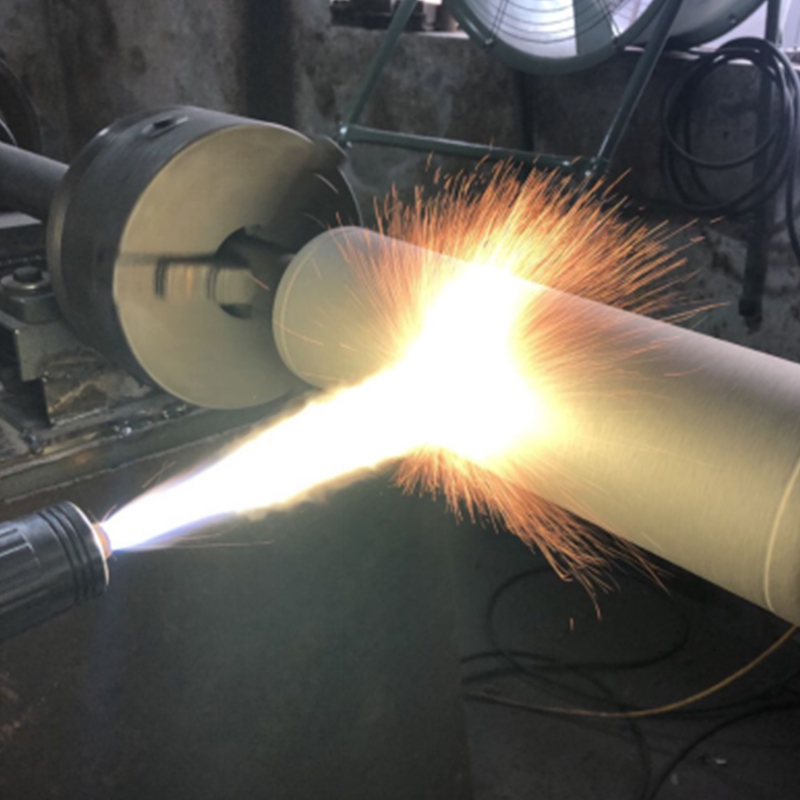
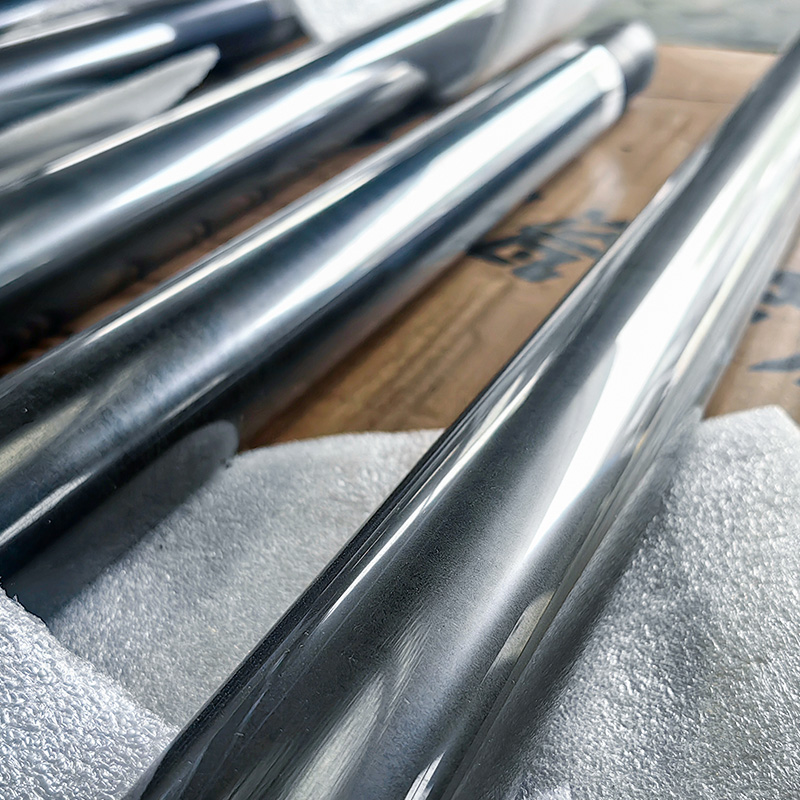
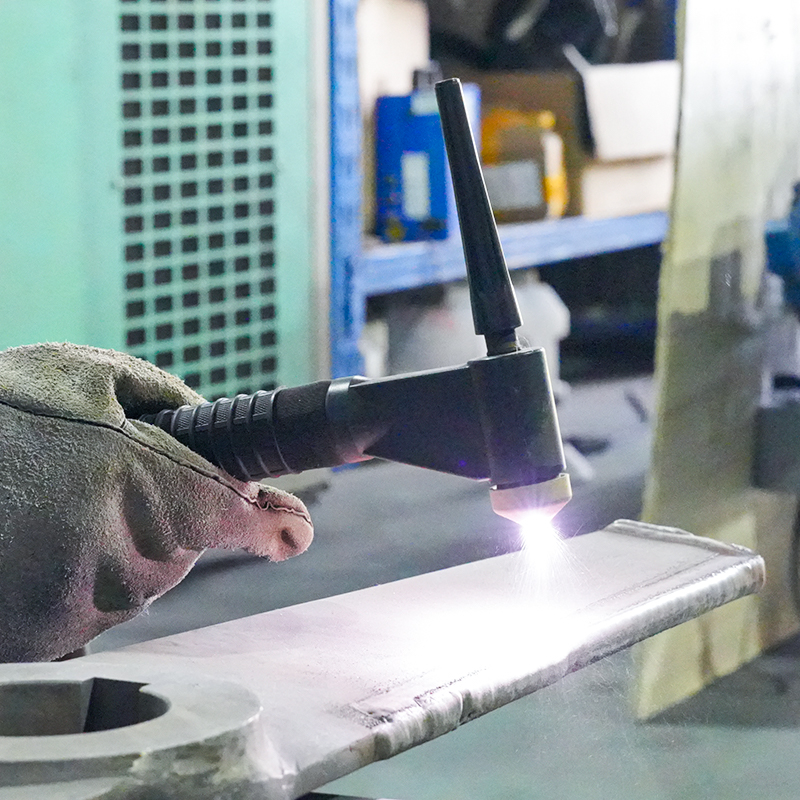
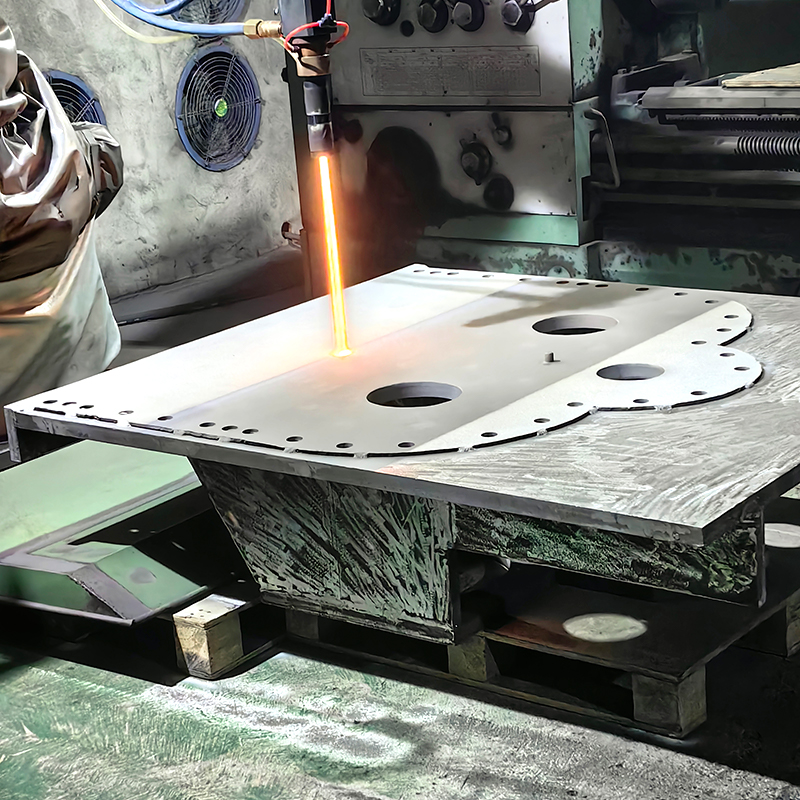
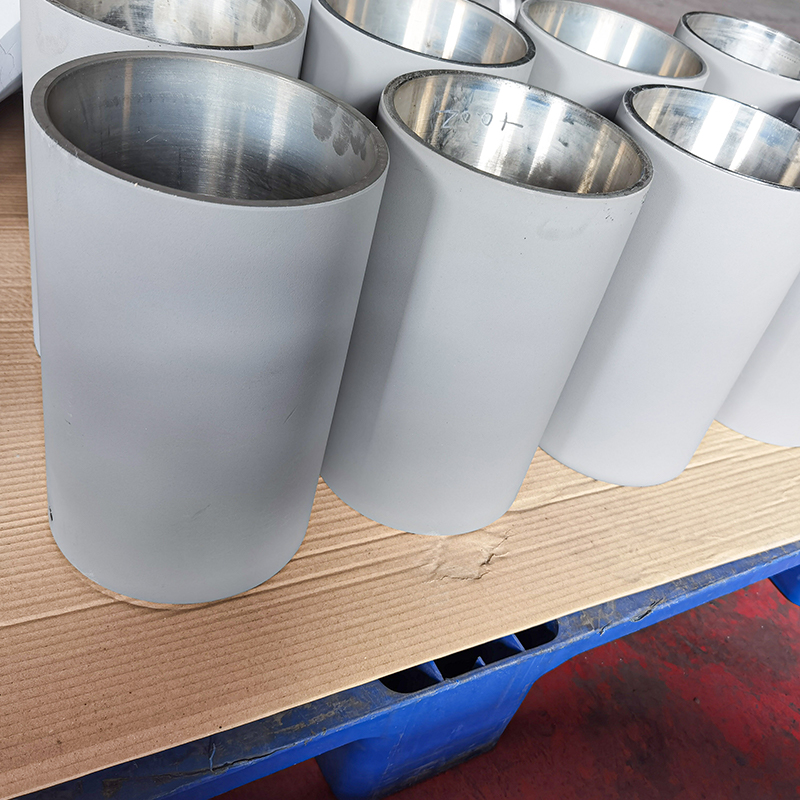
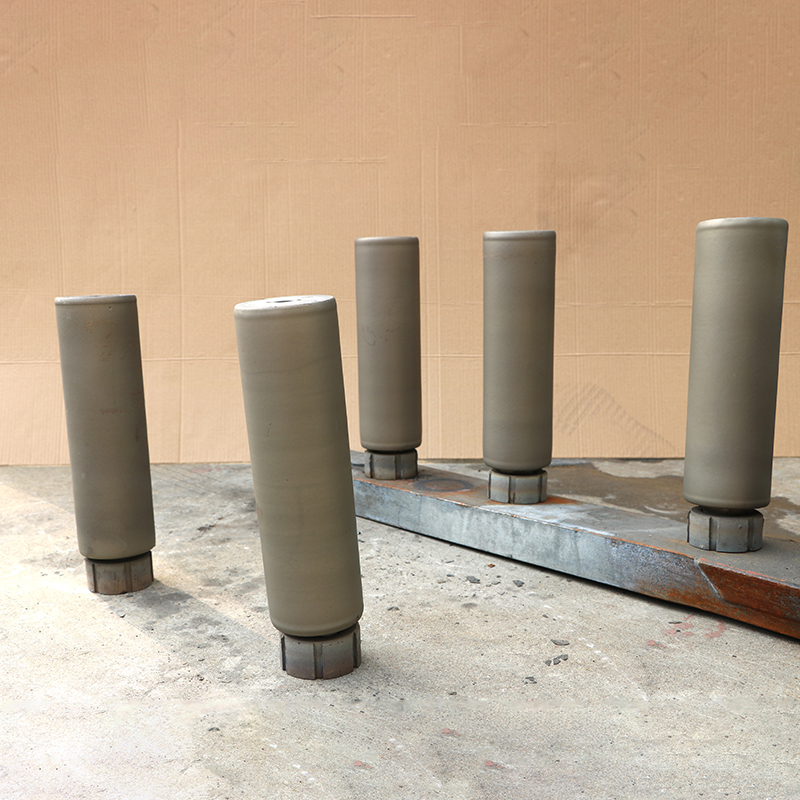
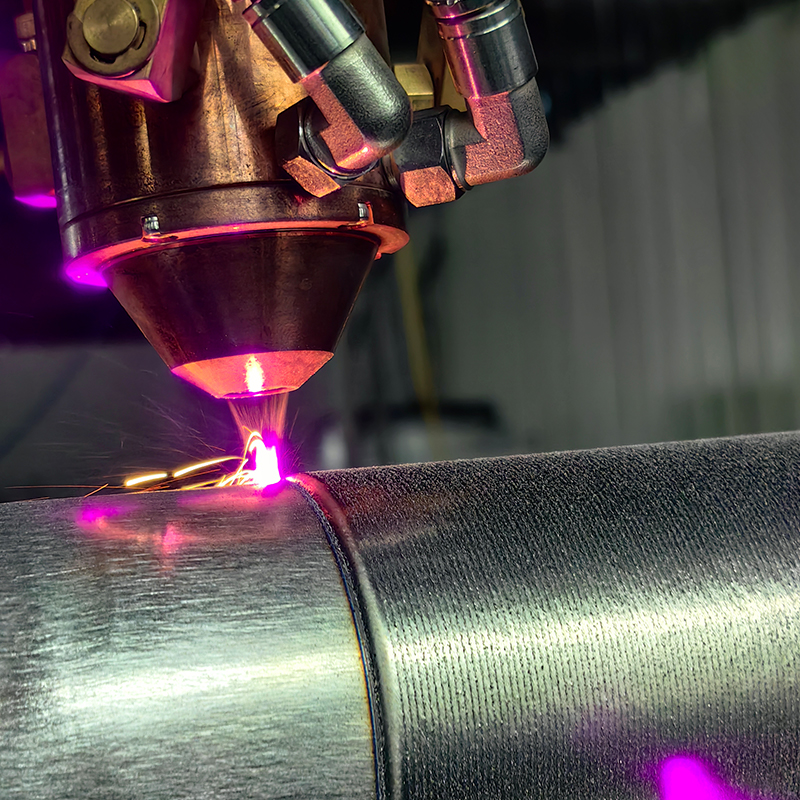
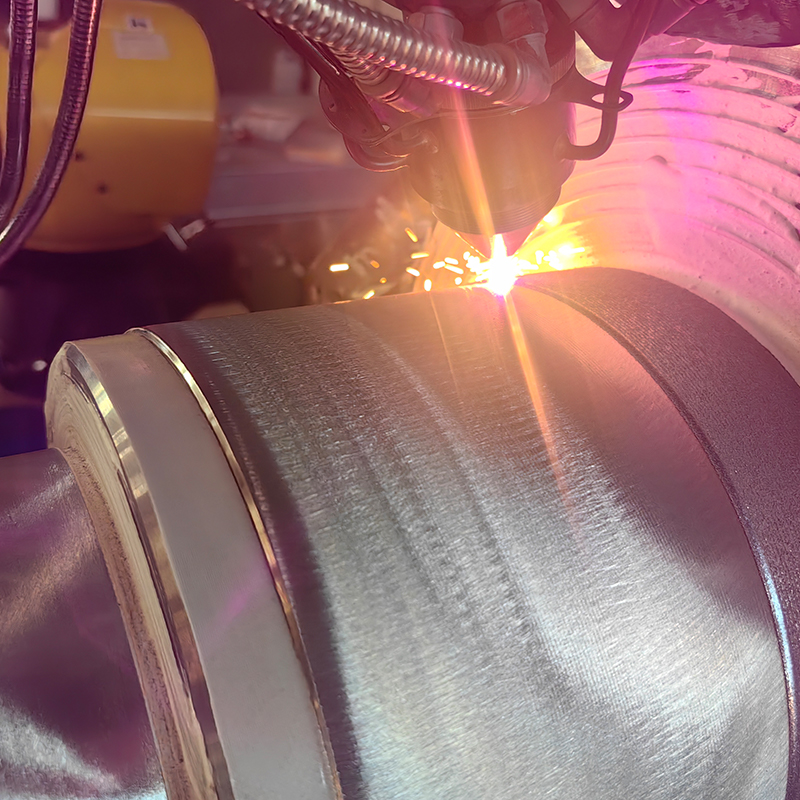
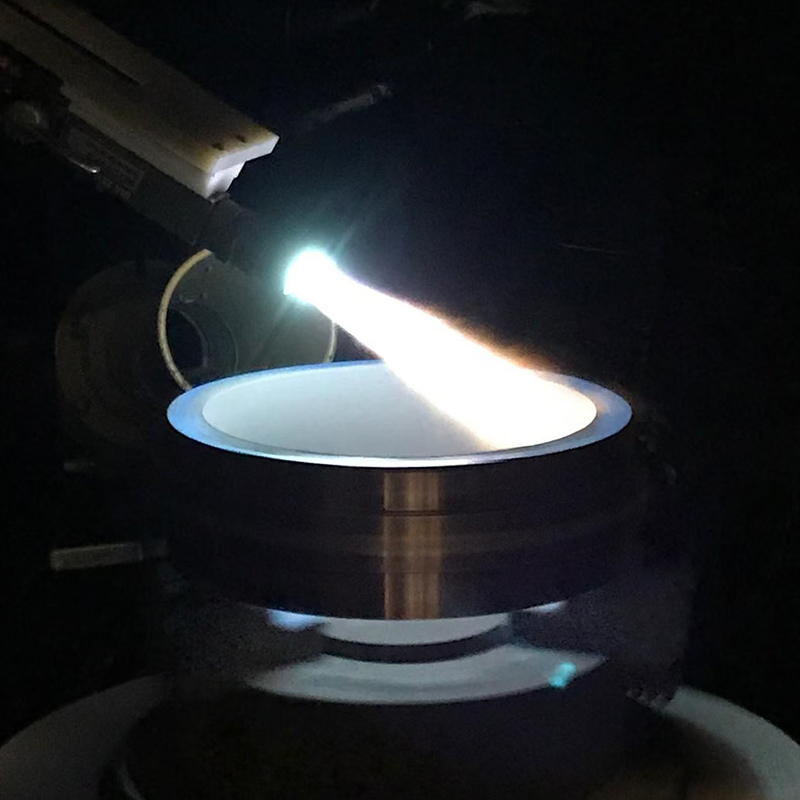
Laser Cladding, also known as laser deposition or laser cladding, is a new surface modification technology. It is a new surface modification technology, which forms a metallurgical additive cladding layer on the surface of the base material by adding the cladding material on the surface of the base material and using the laser beam with high energy density to make it melt with the thin layer of the surface of the base material.
Laser cladding features: low dilution of the cladding layer but the bonding force is strong, and the substrate is metallurgical bonding, which can significantly improve the wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, oxidation-resistant, or electrical properties of the substrate material surface, so as to achieve the purpose of the surface modification or repair to meet the material surface of the specific performance requirements at the same time to save a lot of material costs. Compared with surfacing, spraying, electroplating, and vapor phase deposition, laser cladding has the characteristics of small dilution, dense organization, good combination of coating and substrate, suitable for cladding materials, large changes in particle size and content, etc. Therefore, the application prospect of laser cladding technology is very broad.
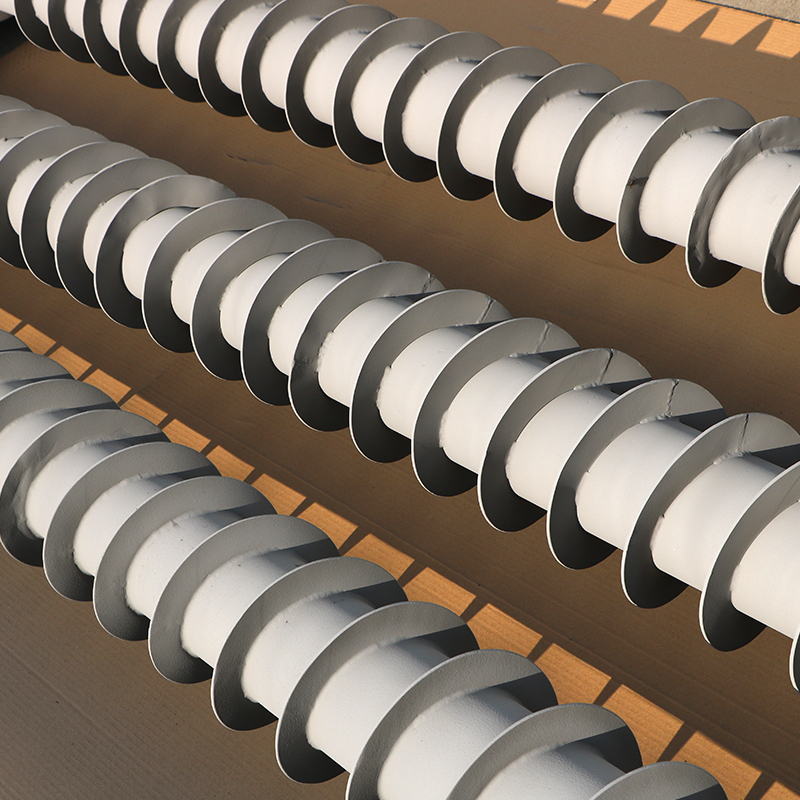
Coating materials: widely used laser cladding materials include: nickel-based, cobalt-based, iron-based, titanium alloys, copper alloys, granular metal matrix composites, ceramic materials, and so on.
Laser Cladding
Powder, (can be customized pure nickel powder, pure cobalt powder, pure copper powder, etc.) metal powder.
We are always committed to developing and producing various high-performance alloy materials for harsh environments, providing customers with high-strength, wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant and high-temperature-resistant alloy powders.
News
-
Industry News 2025-12-24
Advanced Classifications of Copper-Based Alloy Powders Copper-based alloy powders are engineered materials characterized by their high thermal and electrical conductivity, combined with enhanced mechanical properties tai...
View More -
Industry News 2025-12-16
Beyond the Bar: Understanding Cobalt Alloys Cobalt, a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal, is more than just a component in lithium-ion batteries. When alloyed with other elements like chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, or ni...
View More -
Industry News 2025-12-09
The Global Quest for Extreme Durability In the world of manufacturing, mining, and aerospace, nothing is more valuable than durability. Every time a drill bit snaps, a turbine blade erodes, or a bearing wears out, it cos...
View More


 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى